modules:52553_python
| DATA ANALYTICS REFERENCE DOCUMENT |
|
|---|---|
| Document Title: | Applied Databases - Python |
| Document No.: | 1553629016 |
| Author(s): | Gerhard van der Linde, Rita Raher |
| Contributor(s): | |
REVISION HISTORY
| Revision | Details of Modification(s) | Reason for modification | Date | By |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Draft release | Applied Databases - Python | 2019/03/26 19:36 | Gerhard van der Linde |
Topic8 - Python I
Databases vs Program
| Employee ID | Name | Dept | Salary |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | John | HR | 25500 |
| 101 | Mary | R&D | 44500 |
| 102 | Bill | R&D | 43000 |
| 103 | Tom | Sales | 40000 |
SELECT * from employees WHERE Salary > 42000; SELECT * from employees WHERE Salary < 30000;
Variables
- Variables are names areas in the computer's memory that store values.
- variables.py
my1stVariable = "Hello World" my2ndVariable = 1 print(my1stVariable) #Hello World my2ndVariable + 4 print(my2ndVariable) # 1
- Variables are named areas in the computer's memory that store values.
- variables2.py
my2ndVariable = 1 x = my2ndVariable + 4 print(my2ndVariable) # 1 print(x) # 5 age = 21 age = age + 1 print(age) # 22
IF Statements
- ifstatements.py
age = 17 if(age > 17): print("OK") print(finished) # finsied
- ifstatements1.py
age = 17 if(age > 17): print("OK") elif(age < 18): print("Nok") print(finished) #Nok # finished
- ifstatements2.py
temp = 37 if(temp >37): print("Hot") elif(temp <37): print("Cold") else: print("OK") print("Finished") # ok # finished
input
- input.py
name = input("Enter name") # Tom email = name + "@gmit.ie" print(email) # Tom@gmit.ie
- salary.py
salary = input("Enter salary") # 30000 salary = int(salary) salary = salary + 100 print(salary)
WHILE statement
- while.py
i = 1 while(i <=5): print(i) i+=1 # i = i +1 # 1 # 2 # 3 # 4 # 5
- whilebreak.py
answer = "5" while True: guess = input("Pick a number between 1 & 10") if(guess==answer): print("Correct!") break print("end")
Arrays
- array.py
myArr = ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April"] print(myArr) #['Jan', 'Feb', 'March', 'April'] print(myArr[0]) # jan print(len(myArr)) #4
Append()
- append.py
myArr = ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April"] myArr.append("May") print(myArr) ##['Jan', 'Feb', 'March', 'April', "May"]
FOR Statement
- forloop.py
name = ["Tom", "John", "Mary", "Bob"] for name in names: print(name + "@gmit.ie") # Tom@gmit.ie # John@gmit.ie # Mary@gmit.ie # Bob@gmit.ie myArr = [1, 5, 12] for x in myArr: print(x+1) # 2 # 6 # 13 print(myArr) #[1, 5, 12]
User-defined functions
- userfunctions.py
def printMonths(): print("Jan, Feb, Mar") def printDays(): print("Mon, Tue, Wed") printDays() # Mon, Tue, Wed printMonths() # Jan, Feb, Mar
name
- userfunctions.py
def printMonths(): print("Jan, Feb, Mar") def main(): printMonths() if __name__ =="__main__": # execute only if run as a script main()
Parameters
- parameters.py
print("Hello World") # Hello World print("Test") # Test s = "This is a string" print(len(s)) # 16
- parameters1.py
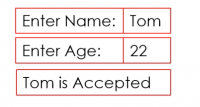
def checkAge(age): if age < 18: return "Too Young" return "Accepted" def main(): name = input("Enter:") age = int(input("Enter Age:")) print(name, "is", checkAge(age)) if __name__="__main__": # execute only if run as a script main()
Local Variables
A local variable is a variable that is given local scope. Local variable references in the function or block in which it is declared override the same variable name in the larger scope.
- localvariables.py
def checkAge(age): limit = 18 if age < limit: return "Too Young" return "Accepted" def main(): name = input("Enter:") age = int(input("Enter Age:")) print(name, "is", checkAge(age), limit) if __name__="__main__": # execute only if run as a script main()
- localvariables1.py
def checkAge(age): limit = 18 if age < limit: return "Too Young" return "Accepted" def main(): limit= "Finished" name = input("Enter:") age = int(input("Enter Age:")) print(name, "is", checkAge(age), limit) if __name__="__main__": # execute only if run as a script main()
Global Variables
- globalvariables.py
def incrementAge(age): age += 1 print(age) # 25 def main(): age = 24 incrementAge(age) print(age) # 24 if __name__="__main__": # execute only if run as a script main()
Declaring the variable outside of the function and using the keword global to make it a global variable
- globalvariables.py
age = 24 def incrementAge(age): # access using the keyword "Global" global age age += 1 print(age) # 25 def main(): incrementAge(age) print(age) #25 if __name__="__main__": # execute only if run as a script main()
Topic9 - Python II
PyMySQL
- MySQLdb
- mysql.connector
- PyMySQL
connect()
- The connect() function connects to a MySQL database.
- host - host where the database server is located
- user - username to log in as
- password - Password to use
- db - Database to use
- port - Port to use
- cursorclass- Custom cursor class to use
Connecting to the Database
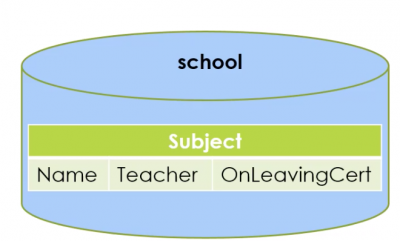
conn = pymysql.connect( "localhost", "root", "root", "school", cursorclass=pysql.cursors.DictCursor)
conn = pymysql.connect( "localhost", "root", "root", "school", cursorclass=pysql.cursors.DictCursor, password="root", host="localhost", db="school", port=3306)
Executing a query
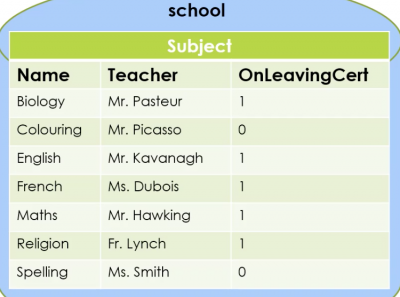
query = "SELECT * FROM subject" with conn: cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(query) subjects = cursor.fetchall() for s in sujects: print(s["Name"])
- query.py
query = "SELECT * FROM subject WHERE teacher LIKE %s" with conn: cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(query, ("Ms.%")) subjects = cursor.fetchall() for s in subjects: print(s["Name"])
Inserting new data
- insertquery.py
ins = "Insert INTO subject (Name, Teacher, OnLeavingCert) VALUE(%s, %s, %s)" with conn: cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(ins, ("Maths", "Ms.Jones", 1)) conn.commit() # commit to database to make a change
try and except block for error messages
- insertquery2.py
ins = "Insert INTO subject (Name, Teacher, OnLeavingCert) VALUE(%s, %s, %s)" with conn: try: cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(ins, ("Maths", "Ms.Jones", 1)) conn.commit() print("Insert successful") except: print("Maths already exists")
Exceptions
name = "Maths" teacher = "Ms.Jones" lc =1 with conn: try: cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(query, (name, teacher, lc)) conn.commit() print("Insert Successful") except pymysql.err.InternalError as e: print("Internal Error", e) except pymysql.err.IntegrityError as e: print("Error", name, "already exists") except Exception as e: print("error", e)
Deleting Data
query = "DELETE FROM subject WHERE name = %s" name = "Maths" with conn: try: cursor = conn.cursor() rowAffected = cursor.execute(query, (name)) conn.commit() if(rowsAffected ==0): print("Nothing deleted - ", name , "never existed") else: print(rowAffected, "row(s) deleted") except Exception as e: print("error", e)
Updating Data
query = "UPDATE subject SET teacher = %s WHERE NAME = %s" subject = "Maths" newTeacher = "Mr.Murphy" with conn: try: cursor = conn.cursor() rowsAffected = cursor.execute(query, (newTeacher, subject)) conn.commit() if(rowsAffected ==0): print(subject, "not updated") else: print(subject, "now taught by", newTeacher) except Exception as e: print("error", e)
Installing PyMySQL
- open command prompt or terminal
- type conda install pymysql
- create a new py file
Topic10 - Python III
pymongo
- client = pymongo.MongoClient()
- client = pymongo.MongoClient(host=“localhost”, port=“27017”)
- try
- client.admin.command('ismaster')
Database and Collections
- mydb = myclient[“cars”]
- cols = mydb.list_collection_names()
- docs = mydb[“docs”]
find()
- people = docs.find({“age”:{“$gt”:18}})
- for person in people:
- print(person[“Name”])
find()
- people = docs.find({“age”:{“$gt”:18}}, {“_id”:0})
- people = docs.find({“age”:{“$gt”:18}}, limit=2)
insert_one()
- newDoc = {“_id”:991, “name”:“John”, “age”:44}
- mycol.insert_one(doc)
insert_many()
- newDocs = [{“_id”:991, “name”:“John”, “age”:44},
- {“_id”:992, “name”:“Mary”, “age”:24},
- {“_id”:992, “name”:“Mary”, “age”:35}]
- mycol.insert_many(newDocs)
Exceptions
- pymongo.errors.ConnectionFailure
- pymongo.errors.DuplicateKeyError
- newDocs = [{“_id”:991, “name”:“John”, “age”:44},
- {“_id”:992, “name”:“Mary”, “age”:24},
- {“_id”:992, “name”:“Mary”, “age”:35}]
- mycol.insert_many(newDocs) mycol.insert_many(newDocs, ordered=False)
delete_one()
- filter = {“age”:{“$gt”:44}}
- mycol.delete_one(filter)
- mycol.delete_one({“age”:{“$gt”:44}})
delete_many()
- filter = {“age”:{“$gt”:44}}
- result = mycol.delete_many(filter)
- DeleteResult
- print(result.deleted_count)
update_one()
- filter = {“age”:{“$gt”:44}}
- update = {“$inc”:{“age”:1}}
- mycol.update_one(filter, update)
update_many()
- filter = {“age”:{“$gt”:44}}
- update = {“$inc”:{“age”:1}}
- result = mycol.update_many(filter, update)
- UpdateResult
- print(result.modified_count)
Review
- MySQL
- MongoDB
- Python
modules/52553_python.txt · Last modified: 2020/06/20 14:39 by 127.0.0.1